Happiness
Influence of Quality Sleep on Physical Well-Being: Unveiling the Power of Restorative Rest
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of physical well-being, influencing various aspects of our health, from muscular repair and immune function to cognitive clarity and emotional resilience.
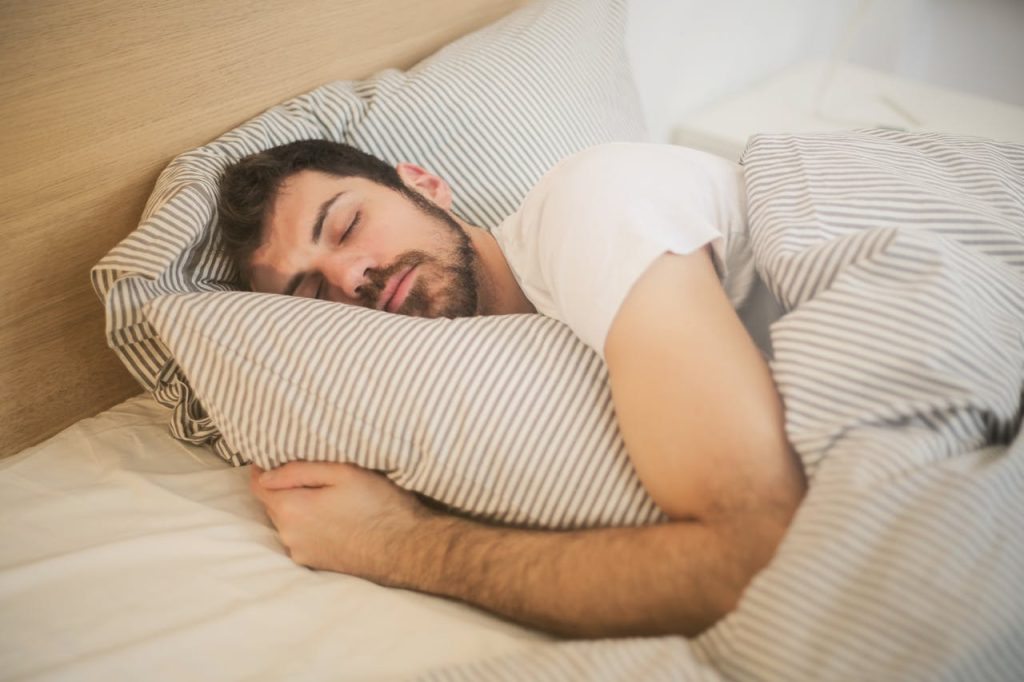

In the fast-paced rhythm of modern life, sleep is often relegated to the background as people juggle work, family, and personal commitments. However, the importance of sleep in physical well-being cannot be overstated. Beyond providing a restorative break from the day’s activities, quality sleep plays a fundamental role in various aspects of our physical health.
We will delve into the intricate relationship between sleep and physical well-being, understanding the mechanisms at play, and uncovering the profound impact that a good night’s sleep can have on overall health.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Sleep Cycle
Before we dive into the role of sleep in physical well-being, let’s explore the basic structure of the sleep cycle. Sleep has two main types-
- Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep.
- Non-REM (NREM) sleep.
Non-REM Sleep:
- Stage 1: Light sleep, transitioning from wakefulness to sleep & this stage usually lasts for some minutes.
- Stage 2: Slightly deeper sleep, characterized by reduced heart rate and decreased body temperature.
- Stages 3 and 4: Deep sleep stages, crucial for physical restoration, muscle repair, and growth hormone release.
REM Sleep:
- Dreaming: REM sleep is associated with vivid dreaming.
- Brain Activity: Heightened brain activity similar to wakefulness.
- Muscle Paralysis: Temporary paralysis of voluntary muscles to prevent acting out dreams.
A complete sleep cycle typically lasts around 90 to 110 minutes, and individuals go through multiple cycles during a full night’s sleep.
Physical Restoration During Sleep
1. Muscle Repair and Growth:
The deep stages of NREM sleep are particularly crucial for physical restoration. During these stages, the body releases growth hormones, essential for muscle repair, growth, and overall development. This is especially significant for individuals engaged in physical activities or athletes, as the repair and growth of muscles occur predominantly during deep sleep.
2. Immune System Support:
Sleep performs a critical function in assisting the immune system. During deep sleep, the body produces and releases cytokines, proteins that assist adjust immune responses. A well-functioning immune system is crucial for warding off infections, and illnesses; maintaining overall health.
3. Hormonal Regulation:
Sleep influences the balance of hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, appetite, and stress. Disruptions in sleep patterns can lead to imbalances in hormones such as cortisol (the stress hormone) and insulin (which regulates blood sugar). Chronic sleep deprivation may contribute to weight gain and an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
4. Cardiovascular Health:
Quality sleep is closely linked to cardiovascular well-being. During deep sleep, the body experiences a decrease in heart rate and blood pressure, giving the cardiovascular system a much-needed break. Consistent sleep deprivation may contribute to hypertension and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
The Impact of Sleep on Physical Performance
1. Exercise Recovery:
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts recognize the importance of sleep in optimizing physical performance. Quality sleep accelerates recovery after intense workouts, aiding in muscle repair and replenishing energy stores. Athletes who prioritize sufficient sleep often experience enhanced endurance, strength, and overall performance.
2. Coordination and Reaction Time:
Sleep deprivation can adversely affect coordination and reaction time. For individuals engaged in activities that require precision and quick responses, such as athletes, drivers, or those operating heavy machinery, adequate sleep is paramount to ensure safety and optimal performance.
3. Endurance and Stamina:
The relationship between sleep and physical endurance is evident in various studies. Athletes who consistently achieve optimal sleep durations tend to exhibit improved stamina, enabling them to sustain peak performance for more extended periods.
4. Injury Prevention:
Adequate sleep contributes to enhanced focus and cognitive function, reducing the risk of accidents and injuries during physical activities. Sleep-deprived individuals may experience impaired judgment and slower reaction times, increasing the likelihood of accidents.
Sleep and Metabolism: Balancing the Equation
1. Appetite Regulation:
Sleep influences the hormones responsible for appetite regulation—ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin stimulates hunger, while leptin signals satiety. Sleep deprivation disrupts this delicate balance, leading to increased hunger and cravings, often for high-calorie, sugary foods.
2. Weight Management:
Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to weight gain and obesity. Poor sleep alters the metabolism of carbohydrates and may lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes. Additionally, sleep deprivation can result in decreased levels of the hormone leptin, contributing to increased fat storage.
3. Circadian Rhythms and Metabolism:
The body’s internal clock, or circadian rhythm, regulates various physiological processes, including metabolism. Disruptions in sleep patterns, such as those experienced with shift work or irregular sleep schedules, can disrupt circadian rhythms, contributing to metabolic imbalances.
The Cognitive Connection: Mental Clarity and Sleep
1. Memory Consolidation:
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation—the process of transferring information from short-term to long-term memory. The various stages of sleep contribute to different aspects of memory, including procedural memory (skills and tasks) and declarative memory (facts and events).
2. Cognitive Function and Creativity:
Quality sleep is linked to improved cognitive function, including enhanced problem-solving skills, creativity, and critical thinking. Sleep-deprived individuals often experience difficulties in concentration, memory recall, and decision-making.
3. Emotional Regulation:
Adequate sleep is essential for emotional well-being and resilience. Sleep deprivation can lead to heightened emotional reactivity, increased stress levels, and a greater susceptibility to mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Establishing Healthy Sleep Habits
1. Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Maintain an everyday sleep timetable with the aid of going to the mattress and waking up at the same time every day, even on weekends. Consistency reinforces the body’s inner clock, selling higher sleep quality.
2. Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine:
Establish a relaxing pre-sleep habitual to sign in your body that it is time to wind down. This may include activities such as reading, gentle stretching, or listening to soothing music.
3. Optimize Sleep Environment:
Create a sleep-conducive surroundings via way of means of preserving the bedroom cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a snug bed and pillows to assist in restful sleep.
4. Limit Exposure to Screens:
Reduce exposure to electronic devices before bedtime, as the blue light emitted can interfere with the production of the sleep-inducing hormone melatonin. Aim to power down devices at least an hour before sleep.
5. Watch Your Diet:
Be mindful of food and drink choices, especially in the evening. Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and immoderate beverages near bedtime, as they could disrupt sleep.
6. Exercise Regularly:
Engage in normal bodily activity, however, the purpose is to finish energetic exercises in advance of the day. Exercise promotes better sleep, but intense activities close to bedtime may have a stimulating effect.
7. Manage Stress:
Incorporate stress management techniques into your daily routine. This may include meditation, deep breathing exercises, or mindfulness practices to alleviate stress and promote relaxation.
8. Seek Professional Help:
If sleep problems persist, consider seeking professional help. A healthcare provider or sleep specialist can identify underlying issues and recommend appropriate interventions or treatments.
The Impact of Sleep Disorders on Physical Well-Being
1. Sleep Apnea:
Sleep apnea, a condition characterized by interrupted breathing during sleep, can have profound effects on physical health. It is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, and daytime fatigue.
2. Insomnia:
Persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep, known as insomnia, can contribute to a range of physical and mental health issues. Insomnia is linked to increased stress, anxiety, and a heightened risk of chronic conditions.
3. Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS):
RLS, characterized by an irresistible urge to move the legs, especially at night, can disrupt sleep and lead to daytime fatigue. Chronic sleep disruption may contribute to mood disturbances and decreased overall well-being.
Importance and Benefits of Sleep from youtube
Embracing the Healing Power of Sleep
Quality sleep is a cornerstone of physical well-being, influencing various aspects of our health, from muscular repair and immune function to cognitive clarity and emotional resilience. Recognizing the profound impact of sleep on physical health emphasizes the importance of prioritizing and optimizing our sleep habits.
In a world that often glorifies productivity and busyness, it is essential to reframe our understanding of sleep as a critical component of a healthy, balanced life. By cultivating healthy sleep habits, addressing sleep disorders, and recognizing the interconnectedness of sleep and physical well-being, individuals can harness the healing power of sleep to optimize their overall health and lead vibrant, fulfilling lives. As we embark on this journey, let us prioritize and celebrate the essential role that quality sleep plays in our pursuit of physical well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
- Why is sleep important for overall well-being?
- Sleep is crucial for physical and mental health. It allows the body to repair, rejuvenate, and regulate various functions, contributing to overall well-being.
- How much sleep do adults need each night?
- Adults typically need 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night for optimal health. However, individual sleep requirements may vary.
- What are the consequences of chronic sleep deprivation?
- Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to various health issues, including impaired cognitive function, weakened immune system, increased risk of chronic conditions, and mood disturbances.
- How does sleep impact mental health?
- Quality sleep is essential for maintaining emotional and mental well-being. Lack of sleep can contribute to stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Can sleep quality affect physical performance?
- Yes, good sleep quality is linked to improved physical performance, including enhanced strength, coordination, and faster recovery after physical activity.
- What role does sleep play in memory consolidation?
- During sleep, the brain consolidates and processes memories. Quality sleep is crucial for optimal cognitive function, learning, and memory retention.
- How does sleep affect weight and metabolism?
- Lack of sleep can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods. It may also slow down metabolism, contributing to weight gain.
- Is it better to maintain a consistent sleep schedule?
- Yes, keeping a consistent sleep schedule helps regulate the body’s internal clock, improving the overall quality of sleep. Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day is beneficial.
- Can electronic devices impact sleep quality?
- The blue light emitted by electronic devices can interfere with the production of the sleep hormone melatonin. It’s recommended to limit screen time before bedtime for better sleep.
- Are naps beneficial for overall well-being?
- Short naps (20-30 minutes) can be beneficial for alertness and performance, but long or irregular napping during the day may disrupt nighttime sleep.
- What are some tips for improving sleep hygiene?
- Establishing a bedtime routine, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants like caffeine before bedtime are some essential tips for better sleep hygiene.
How to improve your sleep : Matthew Walker from youtube-
Wellness
The Healing Canopy: How Nature Enhances Our Well-being
Welcome to a deep exploration of nature’s impact on mood and well-being, a timely reminder of our intrinsic link to the land, the sea, and the sky.

In our bustling, technology-laden world, the call of the natural world often goes unheard. Yet, across the ages, nature has served as a sanctuary, a place of renewal and reflection, inspiring poets and philosophers to extol its virtues and instruct us to ‘stop and smell the roses.’ But what science now reveals is that the sentiment behind these age-old adages is more than mere romanticism; it’s rooted in health and happiness.
Welcome to a deep exploration of nature’s impact on mood and well-being, a timely reminder of our intrinsic link to the land, the sea, and the sky.
Recognizing the Human Connection to Nature
It’s a connection as old as time—humankind’s unbreakable bond with the natural world. Ancient civilizations viewed nature not merely as a provider but as a deity, a source of wisdom and a mirror to the soul. Today, this connection remains, resonating within each of us, waiting to be rekindled.
The essence of this connection has been woven into the cultural fabric of peoples across the globe. Whether in the tranquil Zen gardens of Japan or the windswept moors of England, nature’s influence is undeniable.
The Historical and Cultural Significance of Nature
From the Garden of Eden to the legends of forests and oceans, nature has played a pivotal role in diverse cultural narratives. Throughout history, people have sought solace and community amongst the trees, attributing healing powers to natural springs and caves. The use of herbal medicine and the belief in natural cycles of life and death attest to the pervasive influence of nature across traditions.
The Science of Nature Therapy
The burgeoning field of ecotherapy is a testament to how far we’ve come in understanding and prescribing nature’s balm. Researchers now investigate the psychological and physiological benefits of being in natural environments, with studies pointing towards significant reductions in stress and increased well-being.
Exploring the Field of Ecotherapy
Ecotherapy, or nature therapy, encompasses various practices that merge the healing potential of the outdoors with therapeutic techniques. It aims to improve mental health, emotional well-being, and physical health, delivering a holistic approach to healing.
The Psychological and Physiological Benefits of Nature Exposure
Time spent in nature has been linked to improvements in mood and mental clarity. This experience, known as being in a state of ‘flow,’ where one is effortlessly engaged with their surroundings, can lead to a cascade of positive psychological effects.
Nature as a Stress Reliever and Mood Enhancer
Stress—it’s the ubiquitous malaise of modern life. However, nature appears to hold a restorative power. Whether it’s the sound of waves lapping on the shore or the sight of a majestic forest, natural environments have been shown to calm the mind and elevate mood.
The Role of Nature in Alleviating Anxiety and Depression
The prevalence of anxiety and depression has grown in tandem with our modern, screen-centric lifestyles. Yet, there is compelling evidence that nature exposure can alleviate symptoms. One study found that a 90-minute nature walk reduced activity in the area of the brain linked with depressive rumination.
Connecting with Nature for Improved Cognitive Function
The benefits of nature go beyond the emotional—our cognitive function also reaps the rewards. Nature walks have been shown to improve attention and working memory performance in individuals diagnosed with depression.
The Healing Power of Natural Environments
In the quiet power of a sunrise or the gentle caress of a breeze, we find healing. Natural environments offer a non-pharmacological approach to enhanced well-being that has been harnessed by individuals and healthcare professionals alike.
Therapeutic Effects of Natural Landscapes
The idyllic landscapes of mountains, forests, and coasts are more than a mere feast for the eyes. They are settings for psychological restoration, places where the mind can unwind and rebuild.
The Impact of Green Spaces on Physical and Mental Well-being
Urbanization has brought us indoors and away from the green expanse of country fields. However, the integration of green spaces within urban architecture can provide mental and physical health benefits, mitigating the stress of city life.
Nature’s Contribution to Physical Well-being
We are physical beings, and nature provides the ultimate gym—a vast expanse for walking, running, climbing, and playing. Physical activity in natural settings is not only enjoyable but also reinvigorating for body and soul.
Outdoor Activities and Physical Exercise in Natural Settings
The options for outdoor physical activity are as diverse as the natural world itself, from the vigorous exertion of mountain biking to the gentle flow of roadside yoga.
The Role of Nature in Boosting Immune Function
The practice of ’forest bathing,’ or shinrin-yoku, a leisurely and mindful walk through the forest, has been found to enhance immune response. Spending time in nature exposes us to a rich array of beneficial microorganisms that can strengthen our immune system.
Nature’s Influence on Sleep Quality and Restoration
The connection between exposure to natural light and our circadian rhythms is well-documented. Those who engage with nature regularly often report improved sleep patterns and a deeper sense of rejuvenation upon waking.
Nature, Stress Reduction, and Cortisol Levels
The stress hormone, cortisol, is an omnipresent marker of our body’s response to tension. Studies have shown that activities in natural settings lead to a decrease in cortisol levels, suggesting that nature can serve as a potent stress-reliever.
Creating Tranquil Spaces for Stress Relief
Lush gardens and serene parks provide oases in the midst of urban stress. The incorporation of nature into the built environment through green infrastructure can also provide respite for city-dwellers.

Incorporating Nature Breaks into Daily Routines
Finding time for nature breaks, whether a brief pause to admire a flowering tree or a 15-minute stroll in the local park, can be crucial for managing the daily pressures of life.
Biophilia: Innate Connection to Nature
Biophilia, a term coined by Edward O. Wilson, recognizes our instinctive affiliation with nature. This primal bond has implications for our mental, physical, and social well-being.
Understanding the Biophilic Instinct
Biophilia is more than a vague feeling of comfort in nature—it’s an evolutionary response that urges us to seek out and connect with natural forms and processes that ultimately enhance our sense of well-being.
Exploring Biophilic Design in Architecture
Biophilic design principles are becoming staples in architectural innovation, as designers create spaces that echo the vitality and tranquility of nature, promoting a healthier, happier human experience.
The Impact of Nature-Inspired Spaces on Well-being
Workplaces, hospitals, and homes that integrate elements of nature, such as natural light, greenery, and natural materials, have been associated with improved recovery times, increased productivity, and decreased mental fatigue.
Nature and Social Well-being
Our engagement with nature is often shared, fostering social connections among like-minded individuals. Communities born of these shared experiences often demonstrate a stronger, more cohesive bond.
Shared Nature Experiences and Social Connection
Group hikes, community gardens, and environmental projects can strengthen social networks, creating a sense of belonging and support.
Nature’s Role in Strengthening Community Bonds
Communities that engage with nature together tend to have a stronger communal identity and solidarity, contributing to greater resilience and social well-being.
Nature-Based Activities for Families and Groups
Families and groups that engage in outdoor activities build memories, shared values, and stronger relationships, underlining nature’s influence on the complex tapestry of human social life.
Nature and Creativity
Art and innovation often find their genesis in the great outdoors. The expansive vistas, intriguing patterns, and profound silence of nature offer fertile ground for creative inspiration.
The Inspirational Power of Natural Settings
Visual artists, writers, and musicians have long sought inspiration from nature’s splendor, harnessing its majesty to create timeless works of art.
Creativity and Problem-Solving in Natural Environments
Studies have suggested that even the simple act of walking in nature can enhance creative problem-solving skills, offering a fresh perspective and new ideas.
Nature’s Influence on Artistic Expression
The stylistic elements of various art forms often reflect nature’s influence, from the expressive brush strokes of Impressionist paintings to the tranquil notes of ambient music, bridging the gap between human creativity and the natural world.
Access to Nature in Urban Environments
For a growing majority, urban life is the norm, but this need not signify a complete disconnection from nature. Urban green spaces and carefully designed natural features can offer crucial access points to the outdoor world.
The Importance of Green Spaces in Cities
City parks and gardens are more than mere decorations; they are essential components of a healthy urban ecosystem, providing places to relax, exercise, and socialize.
Urban Planning for Nature Integration
Forward-thinking urban planners are finding innovative ways to harmonize the built environment with the natural, incorporating rooftop gardens, green walls, and public green spaces.
Community Initiatives for Bringing Nature to Urban Dwellers
Local groups and governments often spearhead initiatives to cultivate green areas within urban landscapes, creating opportunities for residents to engage with nature without leaving the city.
Mindful Nature Practices
Mindfulness, the practice of being present in the moment, finds a profound ally in nature. From the intricate dance of leaves in the wind to the sound of birdsong, nature serves as a catalyst for deeper presence and awareness.
Incorporating Mindfulness in Nature Exploration
Mindful nature practices encourage a heightened awareness of one’s surroundings. Techniques such as deep breathing, grounding exercises, and sensory awareness can foster a mindful connection to nature.
Nature Meditation and Mindful Walking
Meditation in natural settings can deepen the practice, with focused attention on the environment leading to a more robust and integrated experience.
Mindful Observation of Natural Elements
Mindfully observing natural elements can lead to a richer understanding of the world around us, fostering a sense of interconnection and awe.
Nature and Seasonal Changes
Nature’s rhythms are cyclical, and our well-being is intrinsically linked to these seasonal shifts. Each season offers its unique gifts and challenges, which we can adapt to and learn from.
Adapting Well-being Practices to Different Seasons
Tailoring our well-being practices to the seasons can align us with nature’s cycles, promoting harmony and health. Winter may call for more reflective activities, while summer may inspire more active pursuits.
Embracing Seasonal Activities for Mood Enhancement
Engaging in seasonal activities, such as gardening in spring or skiing in winter, can invigorate our senses and elevate our spirits.
Nature’s Lessons on Change and Resilience
Observing the changes in nature can teach us valuable lessons about adaptability and the beauty of transformation, preparing us for life’s inevitable shifts.
Nature Conservation and Personal Well-being
Our pursuit of well-being is inextricably linked to the health of our planet. Engaging in conservation efforts not only benefits the environment but also enriches our own lives.
The Reciprocal Relationship Between Nature and Humans
The principle of reciprocity is evident in our relationship with nature; as we care for the earth, it, in turn, nurtures us. This understanding can inspire a more intimate and responsible connection with our planet.
Engaging in Conservation for Environmental and Personal Health
Conservation work offers a dual advantage, promoting environmental stewardship while allowing individuals to experience the joy and satisfaction of contributing to a greater good.
The Ethical Imperative of Protecting Nature for Future Generations
The imperative to safeguard nature for future generations is a call to action for personal and collective responsibility, ensuring the continuation of its bountiful gifts.
Success Stories and Personal Transformations
Real-life accounts of nature’s impact on well-being are both inspiring and relatable. Tales of personal transformation underscore the profound influence of the outdoors on our mental and physical health.
Positive Changes in Mental and Physical Health
Individuals share how their lives have been enriched by nature, whether it’s through weight loss from hiking, improved mood from daily nature walks, or overcoming depression through sustained engagement with the outdoors.
Practical Tips and Lessons Learned from Nature Therapy
Firsthand experiences often yield practical insights and tips for others looking to integrate nature into their well-being routine, from the best times to engage with nature to the most beneficial activities to pursue.
The Future of Nature and Well-being
As we look to the future, one thing is abundantly clear—nature must be a centerpiece of our approach to holistic health. The movement towards greater nature connection is not a trend but a necessity for the well-being of individuals and the planet alike.
Inspiring a Global Movement towards Nature Connection
Experiences shared in this post can inspire others to seek their place under the healing canopy of nature, tapping into its potential for transformation.
The Ongoing Exploration of Nature’s Profound Influence on Human Well-being
Research into nature’s impact on health is an evolving field, with much yet to discover. The ongoing exploration of this topic presents an opportunity for continuous learning and growth.
Encouraging Readers to Embrace Nature for Improved Well-being
This deep-dive into the effects of nature on mood and well-being is a firm call to action for readers to prioritize their connection with the natural world. Its teachings can guide us to a more balanced, grounded, and joyful existence.
Summarizing the Transformative Impact of Nature
The myriad ways in which nature can improve our lives serve as a testament to its importance in shaping our health and happiness. By understanding and harnessing the power of nature, we take a step towards a more vibrant and fulfilling life.
From the tranquil woodland to the majestic mountain, from the vast ocean to the fertile meadow, nature awaits, ready to offer its ageless wisdom and immeasurable gifts. It’s time to listen, to return to our roots, and thrive under the nurturing canopy of the great outdoors.
Happiness
Happiness at Work: Strategies for a Positive Workplace
In a world where the line between personal fulfillment and professional success is increasingly blurred, the pursuit of happiness at work has transformed from a mere aspiration to a strategic imperative.

In a world where the line between personal fulfillment and professional success is increasingly blurred, the pursuit of happiness at work has transformed from a mere aspiration to a strategic imperative. Organizations are now keenly aware that an employee’s emotional well-being profoundly impacts their performance, innovation, and overall job satisfaction. But what does it take to create a truly happy and fulfilling workplace? This comprehensive guide outlines a variety of strategies to foster a positive culture where employees thrive, and organizations flourish.
Table of Contents
The Transformative Power of a Happy Workplace
Workplace happiness is not just about spreading joy; it transcends the daily grind, directly influencing bottom-line figures and company reputation. Employee turnover, absenteeism, and disengagement are costly to any organization. In contrast, happy employees are more productive, creative, and loyal. Research consistently shows that investing in employee well-being is a long-term investment that pays off multifold.
Engaging long-form content aimed at providing value, driving traffic, and enhancing SEO
It’s clear that employee happiness is not a fleeting trend or a ‘feel-good’ initiative. Instead, it’s a cultural ethos that must be woven into the fabric of the organization.
Crafting a Culture of Positivity
Organizational culture is often described as the personality of a company. It includes the company’s values, beliefs, and behaviors — the very elements that can shape whether employees love or dread coming into work each day. By embedding positivity into the culture, employers can ensure that happiness becomes an integral part of their employee’s experience.
Leadership plays a pivotal role in setting the tone for workplace happiness. Encouraging open communication, modeling desired behaviors, and ensuring fairness in how employees are treated are fundamental steps. But it’s the collective responsibility of every team member to nurture and protect the positive culture.
The Gratitude Advantage of Happiness at Work
Gratitude has the remarkable ability to transform our mindset. Feeling appreciated for our work creates a sense of pride and value. Recognizing and appreciating employees can take various forms, from simple verbal acknowledgments to structured recognition programs. The key is consistency and sincerity.
Organizations that make gratitude a core value in their culture reap the benefits of higher morale, engagement, and retention. Through consistent displays of appreciation, companies can effectively communicate that their employees are more than just cogs in a machine — they are valued contributors to the company’s success.
Balancing Act: Work and Life
In our hyper-connected world, the lines between work and personal life can easily blur, leading to burnout and decreased job satisfaction. Striking a balance that allows employees to fulfill their professional responsibilities while also tending to personal needs is crucial for sustained happiness.
Flexible work arrangements can play a significant role in achieving work-life balance. These include options such as telecommuting, compressed workweeks, or flexible hours. By affording employees the autonomy to manage their schedules, organizations demonstrate trust and empower individuals to take control of their work-life integration.
Fostering Strong Team Dynamics
A strong team is more than the sum of its parts — it’s a source of support, inspiration, and camaraderie. Building these dynamics requires a conscious effort to foster trust, encourage collaboration, and celebrate collective achievements.
Team-building activities are one way to achieve this, but the real work happens daily, through communication, shared goals, and mutual respect. A supportive and inclusive team culture not only enhances job satisfaction but also enables employees to contribute their best.
Communication: The Foundation of Happiness
Effective communication is the bedrock of any happy workplace. Clear expectations, open dialogues, and transparent decision-making processes ensure that employees feel informed, involved, and valued.
When leaders prioritize transparent communication, they create an environment where honesty is expected and feedback is constructive. This sets the stage for continuous improvement, empowerment, and growth.
Growth and Learning Opportunities
One of the most significant contributors to workplace happiness is the ability to grow professionally. Investing in training, mentorship programs, and career development shows employees that their organization is invested in their future.
Providing a clear path for advancement and encouraging continuous learning not only prepares employees for future roles but also ensures that they remain engaged and motivated in their current positions.
Programs for Health and Wellness
A healthy employee is a happy employee. Programs that promote physical and mental well-being, such as gym subsidies, meditation classes, or flexible wellness days, demonstrate an organization’s commitment to its employees’ holistic health.
Beyond the traditional wellness offerings, creating a work environment that supports healthier choices, such as standing desks or healthy snack options, reinforces the importance of well-being as a priority.
The Pursuit of Purpose
When work aligns with personal values and contributes to a greater cause, employees find deeper fulfillment and satisfaction. Organizations that articulate a compelling mission and help employees see their role in achieving it can turn a job into a calling.
Encouraging a sense of purpose in daily tasks through storytelling, context setting, and recognition of meaningful contributions can inspire a more dedicated and engaged workforce.
Flexible Work Environments
The concept of the workplace has evolved, especially in light of recent global events. Remote work and flexible arrangements have gone from perks to necessities, and understanding how to effectively manage and motivate a dispersed workforce is key to maintaining a positive culture.
Creating spaces, whether physical or virtual, that support collaboration, focus, and well-being is crucial. It’s about providing the tools and resources for employees to succeed, regardless of their location.
Recognizing Individual Triumphs
While team success is a significant morale booster, recognizing individual achievements is equally important. This personal touch in recognition demonstrates a deeper understanding and appreciation for unique contributions.
Tailoring how individuals are celebrated to their preferences and personalities can make these moments even more powerful, reinforcing the culture of acknowledgment and support.
Navigating Conflict with Emotional Intelligence
Conflict is an inevitable part of any workplace. Developing the emotional intelligence to understand and manage conflict in constructive ways is a valuable skill that can prevent unhappiness from festering.
By approaching conflicts with empathy, active listening, and a focus on resolution rather than blame, organizations can transform adverse situations into opportunities for growth and improved relationships.
Empowerment and Autonomy
Empowered employees feel trusted, capable, and responsible for their work. This sense of ownership drives engagement and innovation, contributing to overall workplace happiness.
Encouraging autonomy doesn’t mean relinquishing control; it’s about creating an environment where employees feel empowered to take the lead, make decisions, and drive initiatives.
The Social Element of Work
Humans are social creatures, and our need for connection extends into the workplace. Encouraging socialization through team events, support networks, and shared moments can boost morale and create a more cohesive work environment.
In the absence of frequent in-person interactions, organizations have to be creative in fostering these connections through virtual water coolers or collaborative technologies that mimic the spontaneity of face-to-face conversations.
Stories of Successful Happiness Initiatives
Real-life examples and stories from organizations that have successfully implemented happiness strategies can be inspiring and instructive. These accounts provide tangible proof that change is possible and offer insights into the practicalities of creating a positive culture.
Examining the keys to the success of these initiatives can help other organizations tailor similar programs to their unique contexts and challenges, ensuring a more personalized and effective approach to fostering happiness at work.
The Continuous Evolution of Workplace Happiness
The pursuit of workplace happiness is not a one-time project but a continuous journey. Trends, technologies, and the needs of the workforce will evolve, requiring a dynamic and responsive approach to maintaining a positive culture.
Organizations must remain vigilant, adaptable, and open to new ideas. By viewing happiness as a dynamic process, leaders can continuously enhance the employee experience and drive sustained performance.
You Don’t Find Happiness, You Create It
Conclusion
Happiness at work is not a lofty ideal but a practical and attainable goal. By embedding these strategies into the daily operations of an organization, employers can significantly impact the well-being and satisfaction of their most valuable asset — their employees. It is through collaborative efforts, a focus on individual needs, and a commitment to continuous improvement that organizations can cultivate a thriving, positive workplace culture. The result?
A workforce that is not only highly productive but genuinely happy and fulfilled. As you consider these strategies, think about how each one could be adapted to your unique workplace and workforce. Start small, and over time, these incremental changes can lead to profound cultural shifts. Your employees will thank you — and so will your bottom line.
Happiness
Laugh More Stress Less: The Power of Humor in Happiness
In the perpetual hustle of modern living, we often overlook one of the most potent antidotes to our stress-filled days—humor. It’s the quintessential elixir that can turn even the most dire moments into opportunities for joy.
In the perpetual hustle of modern living, we often overlook one of the most potent antidotes to our stress-filled days—humor. It’s the quintessential elixir that can turn even the most dire moments into opportunities for joy. This extensive exploration into the largely untapped resource of laughter aims to underscore not only the rib-tickling enjoyment it brings but also the robust framework of benefits it adds to our holistic well-being. Also, we learn that, how to work is laugh more stress less?

Table of Contents
The Universal Language of Laughter
From the raucous chuckles that echo through a bustling comedy club to the subtle, knowing smiles exchanged in a quiet conversation, laughter is a universal language understood by all. It transcends cultural nuances and linguistic barriers, forging connections in its shared expression. The infectious nature of laughter weaves a communal thread, fostering a shared experience of merriment that unites us.
Acknowledging the Connection Between Humor and Happiness
The human experience is replete with opportunities to choose humor over solemnity. These choices, however small, can pave the way for happiness. While humor is not a panacea for all of life’s afflictions, it is an indispensable companion that our minds and bodies greatly benefit from.
Previewing the Positive Impact of Laughter on Stress Reduction
In this post, we’ll dissect the multifaceted relationship between humor and happiness, starting with the unequivocal stress-reducing effects of laughter. You’ll discover the physiological changes that occur in the body when laughter takes over, and how these changes act as a powerful shield against the tide of stress.
The Science of Laughter
Exploring the Psychological Benefits of Laughter
Beyond its surface level of therapeutic joy, laughter triggers a cascade of psychological benefits that linger long after the moment has passed. It releases tension, wards off feelings of despair, and creates a buffer against the everyday worries that ail us.
The Release of Endorphins and Stress Reduction
The physical act of laughing triggers the release of endorphins, nature’s own version of a mood-altering substance. These ‘feel-good’ hormones not only provide instant gratification, but they also promote a sense of well-being that encourages resilience in the face of stress.
Laughter as a Natural Mood Elevator
Additionally, laughter brings with it an influx of oxygen-rich air, promoting a play of neurotransmitters that can elevate our mood. It’s a simple, yet potent, way to counter melancholy, even when it feels most pervasive.
Laughter as a Coping Mechanism
The Role of Humor in Dealing with Life’s Challenges
When life throws us a curveball, humor becomes a defense mechanism, a shield against emotional onslaught. This section explores how humor acts as a powerful ally in confronting challenges, helping us find light in moments of darkness.
How Laughter Acts as a Stress Buffer
Understanding the nuances of how humor buffers us from stress is crucial in leveraging its full potential. We unravel the ways it redirects our focus from worries to the lighter side of life, promoting a mental shift that reduces the impact of stressful situations.
Developing a Humorous Perspective on Adversity
It’s not merely about finding humor in external circumstances; it’s about cultivating a perspective that naturally gravitates towards the humorous, making even the most trying hardships more palatable to our minds and hearts.
Social Bonds Through Laughter
Building Connections Through Shared Laughter
The shared experience of laughter is a potent catalyst for forging connections. Whether with friends, family, or even strangers, the echoes of shared mirth can deepen social bonds in ways that mere words often cannot.
The Importance of Humor in Social Relationships
In this section, we take a deep dive into how humor acts as the social glue that binds relationships. Amidst the rites and rituals of social interaction, it’s often the lighthearted exchanges that resonate most profoundly and create lasting memories.
Creating a Positive Atmosphere in Social Interactions
Laughter energizes social spaces, setting the stage for positive interactions that can uplift not only individual spirits but also the collective mood of a group.
Humor and Physical Well-Being
The Impact of Laughter on Physical Health
Laughter isn’t just good for the soul; it’s a boon for the body. We explore the various ways in which humor can manifest physical benefits, from improved cardiovascular health to enhanced muscle relaxation.
Boosting the Immune System Through Laughter
The relationship between laughter and a robust immune system is no joke. By stimulating antibody cells, laughter becomes a formidable defender against the onset of illnesses, both chronic and acute.
Laughter as a Natural Relaxation Technique
Lauded as a natural relaxation technique, laughter leads to the reduction of stress-related symptoms and the alleviation of muscle tension. It’s as though each bout of laughter is a mini spa day for the body, rejuvenating and invigorating from the inside out.

Incorporating Humor into Daily Life
Finding Humor in Everyday Situations
Life itself is a theater of the absurd, rife with opportunities for finding the humor in the humdrum. This section imparts strategies for tweaking our perspective to notice and appreciate the comedic underpinnings of routine.
Cultivating a Light-hearted Approach to Challenges
Each challenge is an invitation for the clever application of humor. Discover how approaching obstacles with a light touch can transform the most daunting tasks into manageable puzzles, ripe with potential for amusement.
Incorporating Playfulness into Routine Activities
By infusing even the most mundane activities with playfulness and light-heartedness, we can turn daily chores into opportunities for joy. This is the essence of living a life peppered with laughter and an excellent avenue for reducing stress.
Types of Humor and Individual Preferences
Understanding Different Styles of Humor
Not all humor is created equal. Diving deep into the various genres of comedy, we explore the wide spectrum of what tickles the funny bone and why certain styles resonate more strongly with individuals.
Embracing Personal Preferences in Comedy
Each of us has a unique comedic compass that points toward our personal preferences. In this section, we encourage readers to revel in their own brand of humor, asserting that there’s no one-size-fits-all when it comes to laughter.
The Power of Tailoring Humor to Individual Tastes
When humor is tailored to fit individual tastes, it becomes a laser-focused tool for enjoyment and, subsequently, stress reduction. Adaptive humor is not only more effective but also more endearing, creating a more personal and impactful experience.
Laughter Yoga and Therapeutic Laughter
Exploring Laughter Yoga as a Stress-Relief Practice
Rooted in the belief that intentional laughter yields the same benefits as natural laughter, Laughter Yoga is an exercise in mirth that has gained popularity as a wellness practice. We unpack the philosophy behind this unique modality and its potential as a stress-relieving practice.
The Therapeutic Benefits of Laughter Workshops
Laughter workshops offer a structured setting to engage in the act of laughing, with the goal of reaping the many therapeutic benefits. Insights from these workshops underscore the social and emotional aspects of communal laughter.
Integrating Laughter into Mindfulness Practices
Laughter and mindfulness may seem at odds, but when interwoven thoughtfully, they form a sublime tapestry of present-moment joy. This section explores practical ways to integrate laughter into mindfulness practices for an enriched experience.
Humor in the Workplace
Fostering a Positive and Humorous Work Environment
Workplaces that prioritize and allow for humor to flourish are often the most pleasant and productive. Discover the managerial and cultural strategies that cultivate an environment where laughter is embraced.
Using Humor to Improve Team Dynamics
In the realm of teamwork, humor is not just a luxury; it’s a critical component. Teams that laugh together are often the most cohesive, adaptable, and innovative. Explore the ways in which team dynamics can be improved through humor.
The Role of Leadership in Encouraging a Lighthearted Workplace
Leaders set the tone for the work atmosphere. We showcase examples of leadership that have successfully employed humor as a tool for engagement and morale-boosting, inspiring others to follow suit.
Humor and Mental Health
Laughter as a Tool for Managing Anxiety and Depression
When it comes to mental health, laughter is an unsung hero. Its unassuming nature belies its prowess as a coping mechanism for those managing anxiety and depression. We offer practical insights and suggestions for incorporating humor into one’s mental health toolkit.
The Therapeutic Role of Comedy in Mental Health
Comedy isn’t just entertainment; it’s therapy. This portion of the post highlights the role of humor in the mental health industry, from therapeutic stand-up comedy to scripted humor implemented as part of treatment.
Incorporating Humor into Self-Care Routines
Self-care without joy is an incomplete practice. We provide tips for infusing self-care routines with humor, ensuring that they become not arduous tasks, but delightful rituals that contribute to one’s overall well-being.
Comedy and Cultural Expression
The Role of Humor in Cultural Identity
Cultural humor is a defining aspect of identity and community. From classic comedies to cultural memes, we explore how humor becomes a hallmark of shared experiences, history, and aspirations.
Using Comedy for Social Commentary
Comedy has a way of saying what other mediums cannot. We dissect the art of using humor for incisive social critique, praising the comedians who deftly wield their wit to mirror society’s absurdities.
Appreciating Diversity in Humor
An appreciation for humor requires an open mind and a recognition of the diversity of comic sensibilities. We champion the adage that laughter is best when shared, and the more varied the laugh, the richer the experience.
Family Humor and Bonding
Creating a Playful Family Culture
Families that laugh together often stay together in spirit, if not in proximity. Here, we provide strategies for building a family culture rooted in playfulness and a shared love of laughter.
The Influence of Humor on Parent-Child Relationships
Humor can be a parent’s most disarming and effective tool. We explore the delicate balance of using humor to connect with children, fostering deep, meaningful relationships built on mutual respect and joy.
Nurturing a Joyful Family Atmosphere
Joy doesn’t just happen; it’s nurtured. This section is brimming with tips for creating a home environment that resonates with laughter, from family game nights to impromptu joke sessions.
Laughter Challenges and Laughter Clubs
Participating in Laughter Challenges for Community Building
Laughter that ripples across the community can have a profound impact, transcending the individual to uplift the collective. Learn about laughter challenges that have become a gathering point for communities near and far.
The Concept of Laughter Clubs and Group Laughter
Beyond the power of the solo laugh lies the resounding strength of a group’s laughter. Be inspired by the phenomenon of laughter clubs and the sense of belonging they bestow on their members.
Spreading Laughter for Collective Well-being
The notion that laughter is contagious is taken to a larger, even grander level in this section, as we explore how collective laughter can promote a sense of well-being that ebbs and flows throughout a community.
Success Stories and Humor Transformations
Real-life Experiences of Using Humor for Happiness
True stories of individuals who have harnessed humor to overcome their trials and tribulations illuminate the path to a happier life. Prepare to be uplifted and inspired by their narratives of transformation through laughter.
Positive Changes in Mental and Emotional Well-being
Listeners of these tales of transformation will be encouraged to recognize the seeds of humor in their own lives and the potential they hold for change.
Practical Tips and Lessons Learned from Embracing Humor
Derive actionable insights and pearls of wisdom from those who have walked the path towards a more humorous existence. Their pragmatic tips will serve as a compass for your humor-infused journey.
The Future of Happiness Through Humor
Embracing Laughter as a Lifelong Companion
Laughter isn’t merely a temporary reprieve from life’s challenges; it’s a steadfast companion that, when embraced fully, can alter the course of our existence. We look forward to a future where laughter is not just encouraged but expected as an integral part of well-living.
Inspiring a Humorous and Joyful Global Community
Here, we cast a vision of a world where laughter is the common thread that binds us, a world community characterized by its proclivity for humor and the ensuing joy it brings.
The Ongoing Journey of Stress Reduction Through Laughter
The quest for stress reduction through laughter is a lifelong one, punctuated by joyful moments that serve as beacons along the path. We encourage you to keep laughing, keep exploring, and most of all, keep living.
Conclusion
In summary, humor is far more than a reaction to life’s absurdities; it’s a proactive stance, a way of life that can enhance our experience immeasurably.
The evidence is overwhelming—laughter contributes to our health, happiness, and overall well-being. We urge you to take charge of your stress levels and infuse more laughter into your life.
The path to a happier and healthier life is one you tread with each chuckle, chortle, and full-throated guffaw. Join us as we revel in the wondrous, stress-reducing power of humor and commit to its ceaseless cultivation in our lives and communities.
By weaving together practical advice, inspirational anecdotes, and scientific understanding, our exploration into the laughter-laden landscape of human happiness is a testament to the simple magnificence of humor. It’s an invitation to cast off the weight of worry in favor of a more buoyant, laughter-lit existence.
-
 Personal Care8 months ago
Personal Care8 months agoWhy Regular Massages Could Be the Game-Changer Your Body and Mind Crave
-

 Mental Health7 months ago
Mental Health7 months agoHow to Overcome Phobias: 15 Positive Psychology-Based Strategies That Really Work
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoWhen Is It Time To Get a Divorce? Emotional, Mental & Practical Signs to Know
-

 Fitness7 months ago
Fitness7 months ago6 Quick Morning Exercises to Burn Belly Fat All Day
-

 Mental Health7 months ago
Mental Health7 months agoWhat Is A Depression Attack? Symptoms, Causes & How To Cope With One
-

 Lifestyle7 months ago
Lifestyle7 months agoHow to Improve Egg Quality for Fertility: Science, Lifestyle and Expert Tips
-

 Food7 months ago
Food7 months agoHealthy Rice Varieties: Nutrition and Health Benefits
-

 Personal Care7 months ago
Personal Care7 months agoHow to Reparent Your Inner Child: Healing and Self-Compassion



